



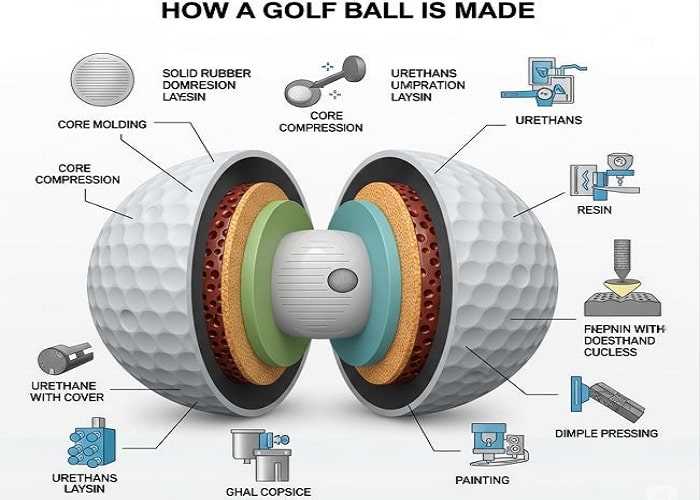
Begin with a core, the beating heart of a sphere, crafted from synthetic rubber or a similar compound. This nucleus is pivotal, as it influences compression and overall performance on the course. The correct formulation of materials is crucial to ensure durability and optimal energy transfer upon impact.
The next stage involves enveloping this core with layers, typically of rubber or ionomer, which enhance aerodynamics and offer a desired spin. Each layer is precisely calculated in thickness and resilience to respond effectively to various swinging speeds and player preferences. The molding process requires high-temperature vulcanization, which solidifies the layers and integrates them seamlessly.
After forming the outer layer, the surface pattern is designed to maximize flight stability. Dimples, strategically placed, minimize drag and contribute to lift during flight. The number of dimples and their arrangement significantly affect distance and control, ensuring that each crafted sphere meets rigorous performance standards.
Color and branding come into play after the structural components are finalized. Inks and finishes are applied carefully to ensure visibility and aesthetic appeal, providing an eye-catching finish. Quality control is paramount throughout the entire manufacturing process, where each unit undergoes rigorous testing to meet specific weight and balance criteria.
Manufacturing Process of Spherical Projectiles
To produce spherical projectiles, initiate with a core usually crafted from synthetic rubber, termed polybutadiene. This core determines the initial feel and compressibility of the item. Varying the density and hardness of the core influences the flight characteristics.
Surrounding the core, apply a layer of resin or thermoplastic material. This layer adds durability and aids in achieving desired spin and distance. The thickness of this covering can be tailored to affect overall performance.
| Material | Function |
|---|---|
| Synthetic Rubber (Polybutadiene) | Core creation, determines feel and compression |
| Thermoplastic | Outer skin, enhances durability and spin |
| Urethane | High-performance cover for control and feel |
After layering, utilize compression molds to shape and solidify these components through heat and pressure. This process establishes the structural integrity and optimizes performance metrics.
Subsequently, a final coating is applied for aesthetics and protection. Quality control measures include testing for uniformity, weight, and resilience to ensure compliance with standards.
Finish by printing logos and numbers using a durable ink method to withstand multiple rounds of play. This comprehensive approach results in a finely tuned projectile that meets varying players’ needs and preferences.
Understanding Core Materials and Their Properties
Selecting the right core material significantly influences the performance of the sphere. Two primary materials are prevalent: rubber and plastic. Each type provides distinct benefits, impacting spin, distance, and feel.
Rubber Cores
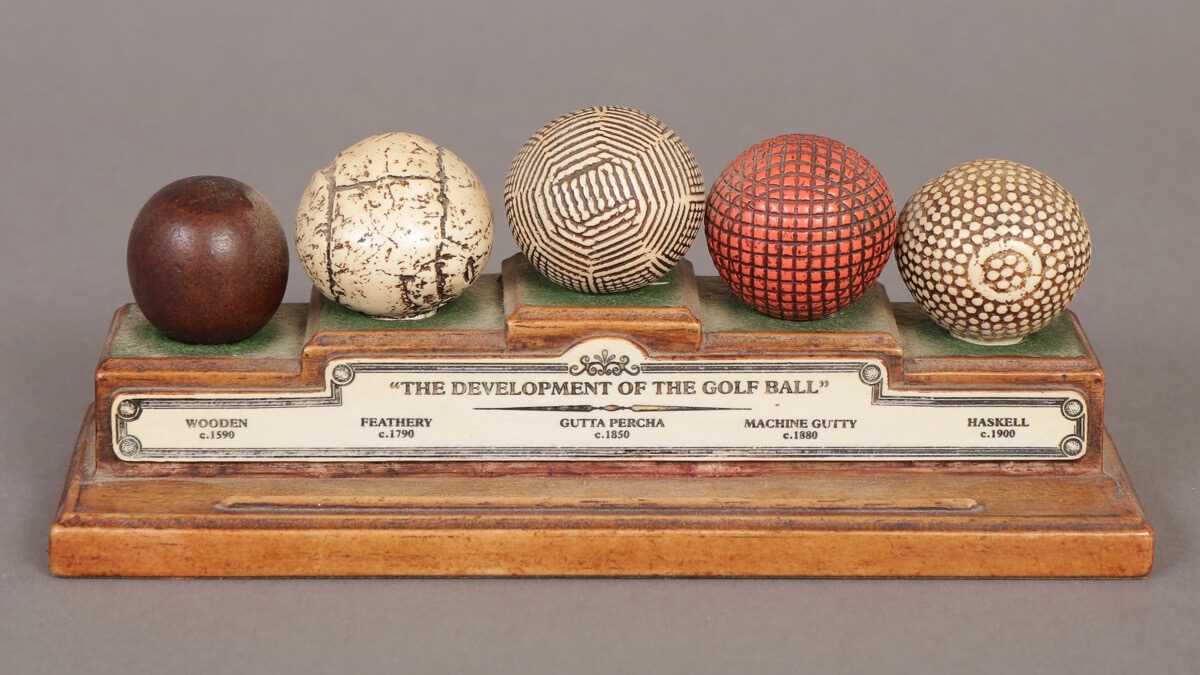

Rubber is often used for its elasticity and resilience. This material enhances energy transfer upon impact, providing superior distance. Key characteristics include:
- Elasticity: Allows for maximum compression, resulting in higher ball speeds.
- Durability: Resistant to wear and tears, maintaining performance over time.
- Control: Offers a soft feel, which aids in shot precision.
Plastic Cores
Plastic cores, particularly those formulated with advanced polymers, are increasingly used for their lightweight nature and manufacturability. Main features entail:
- Lightweight: Facilitates longer distances due to reduced overall mass.
- Consistent Shape: Molds easily into uniform spheres, ensuring consistency in flight.
- Cost-Effective: Generally lower production costs, allowing for greater market accessibility.
An understanding of these core materials is crucial in designing products tailored to specific performance needs, allowing manufacturers to cater to different player preferences effectively.
The Process of Molding the Outer Shell
A precise temperature control system is necessary during the shell formation phase, which employs specialized molds designed for durability and repeatability. The outer layer is typically constructed from materials like urethane or surlyn, chosen for their durability and playability characteristics. The mixture, comprising resin and additives, is heated to a specific viscosity before being injected into the molds.
<h3.Mold Preparation
Before injection, molds undergo extensive preparation. They are meticulously cleaned and preheated to enhance material flow and ensure even distribution during the molding process. A release agent is applied to facilitate the removal of the finished products post-molding.
<h3.Injection Process
The material is injected under high pressure to fill the mold cavity completely, allowing for intricate designs that affect aerodynamics and feel. After injection, the molds are cooled efficiently to solidify the outer layer. This cooling phase is critical, as it can significantly influence the final properties of the surface.
Exploring the Dimple Pattern Design
The dimple pattern significantly influences ball trajectory and performance. A well-engineered surface with dimples enhances lift and decreases drag, allowing for greater distance and control. When designing these patterns, manufacturers consider depth, diameter, and spacing, which can alter airflow dynamics and stability during flight.
Dimples: Types and Their Impact
Common dimple shapes include shallow and deep variations, each providing unique aerodynamic properties. For instance, shallow dimples may produce a softer feel and greater accuracy, while deeper configurations enhance lift, enabling longer yardages. An optimized design often combines these shapes to balance feel, distance, and accuracy.
Testing and Innovation
Continuous testing of dimple designs is vital. Using wind tunnels and computer simulations, engineers analyze airflow patterns around prototype surfaces. Feedback from professional players also informs modifications, ensuring that modern designs meet performance expectations. The pursuit of unique dimple patterns continues, pushing the boundaries of technology in ball sports.
Quality Control Measures in Golf Ball Production
Implement regular inspections throughout the manufacturing stages to ensure product excellence. Utilize automated systems to measure weight, diameter, and overall symmetry. These metrics are crucial for consistency in performance and user satisfaction.
Testing Procedures
Conduct rigorous testing, including compression and rebound tests, to evaluate the resilience and responsiveness of the inner core. Utilize advanced technology to analyze material properties during the molding phase, ensuring optimal performance standards are met pre and post production.
Final Quality Assurance
Before packaging, perform a visual examination to detect any surface imperfections or defects in the outer shell. This additional scrutiny prevents flawed items from reaching consumers, thereby maintaining brand integrity and customer trust.
Environmental Impact in Production of Sphere Shaped Sport Equipment

Utilize biodegradable materials during the creation process. Switching to natural rubber and plant-based polymers reduces reliance on petroleum-based products. This shift not only decreases carbon emissions but also enhances sustainability over the product’s lifecycle.
Implement recycling practices by reclaiming scrap materials from manufacturing. This practice minimizes waste and contributes to a circular economy. Reusing materials not only lowers costs but also conserves resources.
Monitor emissions in factories rigorously. Regular assessments can identify sources of pollution, allowing for timely adjustments to equipment and practices. Additionally, incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, can significantly reduce carbon footprints.
Promote ethical sourcing of raw materials. Establishing partnerships with suppliers who adhere to environmental regulations ensures that materials are obtained without harming ecosystems. This approach also fosters a positive brand image among environmentally-conscious consumers.
Invest in biodegradable packaging for finished products. Packaging represents a significant waste contributor, and using compostable or recyclable options aligns with environmental standards and appeals to a growing demographic focused on sustainability.
Educate stakeholders about eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Training employees and involving them in sustainability initiatives not only bolsters team morale but also enhances production processes through collective ideas and innovation.







